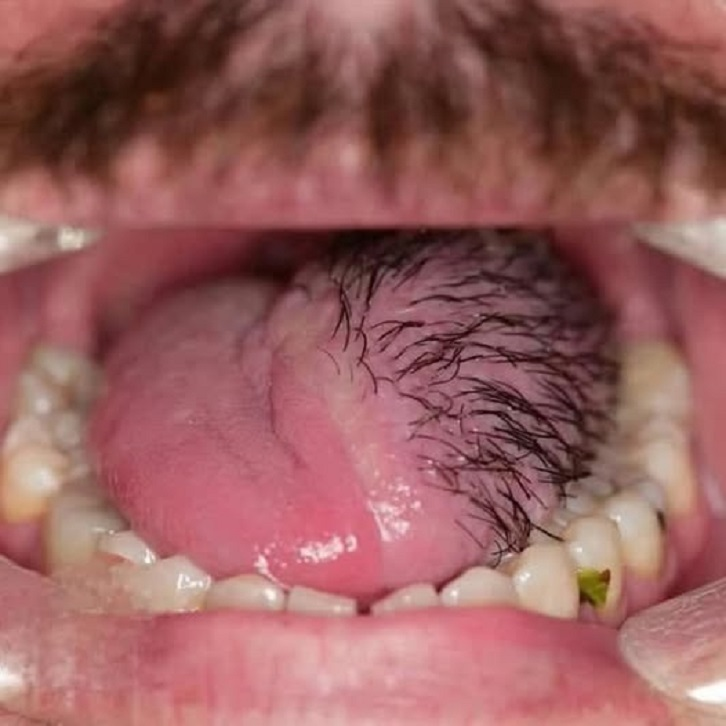
Fungal tongue infections, often caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida, can develop for a variety of reasons. Common factors include poor oral hygiene, prolonged use of antibiotics, and a weakened immune system. When the natural balance of microorganisms in the mouth is disrupted, Candida can thrive.
Common Symptoms
Red, Shiny Tongue:
A smooth, red, and shiny tongue is a noticeable sign. This may come with a burning sensation, which can be worsened by spicy or acidic foods. In some cases, this condition is linked to systemic issues like iron deficiency anemia, which may also cause fatigue.
White or Yellow Coating:
Another sign of a fungal infection is a thick white or yellowish coating on the tongue, often called oral thrush. This can cause mild discomfort and sometimes a persistent metallic taste or bad breath.
Burning Sensation and Taste Changes:
Both red and coated tongues can alter the sense of taste. Foods may taste bland, bitter, or metallic, which can affect appetite and nutrition, especially if the infection is severe or chronic.
Home Care and Prevention
Oral Hygiene:
Brushing your tongue gently twice a day with a soft toothbrush helps remove buildup and reduce fungal growth.
Rinses:
Rinsing your mouth with salt water or a mild baking soda solution can create an environment less favorable to fungal growth.
Diet and Lifestyle:
Limiting sugar and yeast-rich foods, staying hydrated, and maintaining overall oral hygiene can help prevent recurrence. For those on antibiotics, probiotics may support healthy oral flora. People with weakened immune systems should consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
By paying attention to oral health and taking preventive measures, most fungal tongue infections can be managed effectively.